This has been the hot button topic of the year, pretty much everywhere around the globe. Inflation has accelerated in many countries, but at very different rates. Regardless, there has been a general withdrawal from both fiscal and monetary stimulus across both developed and developing countries, though the results remain to be seen.
Before getting into any analysis, this is what inflation in Malaysia looks like (log annual and monthly changes; 2000=100):
For those coming across this for the first time, I generally track inflation via four different indices: the CPI and PPI from DOSM, a core measure that excludes food and transport, and a pain index that is only food and transport. I haven't talked much about the PPI in the past, but I'll include that in a future post because in this particular period, it's quite important. Also, my core measure is slightly different from the one compiled by DOSM, but they're pretty close.
The first and most important point from the chart above is that overall inflation in Malaysia is roughly back to its long term average. The second important point is that it is almost exclusively food and transport that is driving the increase in the price level. Core inflation has also been rising, but nowhere near to the same extent and its also been going up in fits and starts, not a steady continuous rise.
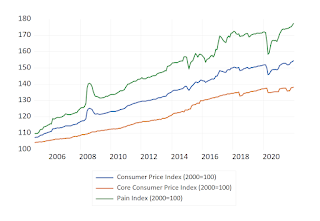
Here's looking at the three indices from a level perspective (2000=100):
Looking at the raw levels is always useful, especially when you get structural breaks in the data (like yes GST, no GST, or a sudden pandemic).
Note that core prices, ie everything but food and transport, has not seen anything like the increase in those prices. A second point is that the steepness of the line for core prices has been relatively flat for the last five years or so. Inflation (the rate of change of prices) is evaluated as the slope of the price index over time, so a flatter slope indicates weak price pressures. All that is rather telling, pointing to weakness in domestic demand generally, even with the slight uptick in the most recent data. The indications are that inflation is Malaysia is being driven by external prices, not domestic pressures.
In the queue after this, delving into national comparisons, theory, empirics, and MMT.
Technical Notes: